GABA – The Neurotransmitter Of Rest And Relaxation
Do you feel excited, irritable, or sad for no apparent reason? Is that a feeling that often comes up in you? While there can be several explanations for this, one possibility is that your brain has low levels of certain substances, primarily neurotransmitters. Our brain uses up to 100 different neurotransmitters, one of the most important of which is GABA, the neurotransmitter for rest and relaxation.
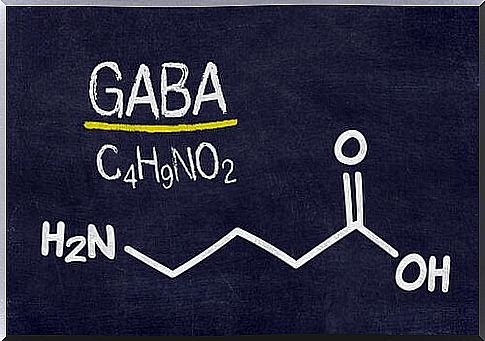
γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an amino acid and neurotransmitter that regulates the excitability of the brain by preventing the excessive firing of neurons, resulting in a feeling of calm. A balance in GABA levels will help reduce stress, be less anxious, and reduce the likelihood of various health problems.
What is GABA and what does it do?
Y-aminobutyric acid is one of the most important neurotransmitters, the messenger substances, through which brain cells communicate with one another. In fact, it is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Inhibitory or inhibitory neurotransmitters generally reduce the likelihood that a nerve impulse will be triggered.
The main function of γ-aminobutyric acid as an inhibitory neurotransmitter is to decrease the activity of neurons. Sleep, muscle tone and motor control, and vision are regulated by GABA, but it is also widely used both inside and outside the central nervous system. It is found in the intestines, stomach, pancreas, liver, spleen, kidneys, urinary bladder, genital organs, lungs, muscles and skin – to name just a few examples.
Diseases and disorders related to GABA metabolism dysfunction include depression, autism, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, some types of dementia (Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal dementia), and diseases characterized by involuntary movement such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, tardive dyskinesia and Huntington’s disease, and fibromyalgia. In addition, some intestinal ailments, such as Crohn’s disease, irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, are also associated with low levels of this neurotransmitter.
One of the most important qualities of γ-aminobutyric acid is its ability to minimize stress and anxiety. When the GABA level is low, the likelihood increases that we feel anxious or overwhelmed and that we are very sensitive to stimuli. With that in mind, an article published in the journal Nature states that this neurotransmitter can target and reduce unwanted thoughts that increase stress, anxiety, depression, and other psychiatric disorders.
Another way γ-aminobutyric acid affects brain activity is by changing brain wave patterns. The presence of GABA increases the brain waves associated with a relaxed state called alpha waves and decreases the beta waves associated with stress and anxiety.
The balance of brain activity
To understand how γ-aminobutyric acid works, another neurotransmitter, L-glutamate, needs to be considered. This neurotransmitter serves as a precursor in the synthesis of GABA and is itself a very important excitatory neurotransmitter. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that a nerve impulse will be triggered.
The two neurotransmitters have a complementary and opposite effect to each other. L-glutamate, the most important excitatory neurotransmitter, offsets the inhibitory effects of GABA. While γ-aminobutyric acid reduces brain activity, L-glutamate stimulates it.
These two neurotransmitters work together to regulate brain activity. Both are required to maintain balance.
Is Your GABA Level Too Low?
In most cases, a dysfunction in GABA metabolism can be directly attributed to lifestyle. With this in mind, says Dr. Datis Kharrazian, researcher at Harvard Medical School (Massachusetts, USA), stress, little sleep, poor diet, too much caffeine and gluten intolerance are the most common causes of such disorders. In fact, caffeine inhibits the activity of γ-aminobutyric acid, while alcohol and sedatives increase it.
It should also be noted that intestinal bacteria can produce this neurotransmitter, so that dysbiosis, i.e. an imbalance between the “good” and “bad intestinal bacteria”, can limit the production of γ-aminobutyric acid. In addition, it should be taken into account that excess L-glutamate is converted into GABA with the help of vitamin B6 and the enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. This can result in a deficiency in vitamin B6 or an autoimmune reaction against one of the parties involved. affect GABA production. Autoimmune diseases, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, diabetes mellitus, and celiac disease, are responsible for such autoimmune reactions.

How can you increase your GABA level?
There are dietary supplements that contain a synthetic form of this neurotransmitter. However, there is controversy over whether these remedies really work. We don’t know if they reach the brain in amounts large enough to have any effect. While some people feel better after using these drugs, this may be due to a placebo effect. We also have little knowledge of possible side effects of consumption, so we do not have enough information to guarantee the safety of these dietary supplements.
However, there are many other ways you can naturally maintain healthy levels of GABA. One of these options is eating healthy. In this context, a study by the Institute of Biosciences at the University of Cork in Ireland found that probiotic foods increase the level of γ-aminobutyric acid. Food such as yogurt, kefir, kimchi and sauerkraut contain the bacterial strains Lactobacillus brevis and Bifidobacterium dentium , which are particularly suitable for this.
Also, if you are concerned about your GABA levels, it is important to minimize your caffeine intake as it inhibits this neurotransmitter’s ability to bind to its receptors. Instead, you can drink tea that contains less caffeine but the amino acid L-theanine, which has a positive effect.
It should be noted that another very effective way to increase GABA levels is through exercise. Any kind of exercise increases the level of this neurotransmitter – we recommend yoga. In fact, levels of this neurotransmitter in the brain can increase significantly after a single yoga session.









